Malintha Fernando
Digital Futures Postdoctoral Fellow
KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Sweden

I am a researcher interested in multi-agent systems, aerial swarms and reinforcement learning. I will join the KTH Royal Institute of Technology this fall as a Digital Futures Postdoctoral Fellow to continue my research in designing multi-objective reinforcement learning strategies for robotics teams. I will be working in between the division of optimization and systems theory in the department of Mathematics, and the division of robotics, perception and learning in the department of Intelligent Systems.
Before joining KTH, I worked as a lecturer at the department of Intelligent Systems Engineering of Indiana University”.
News
| Feb, 2024 | Excited to announce that I have been awarded the Digital Futures Postdoctoral Fellowship by the KTH Royal Institute of Technology ($200,000/SKR 2,000,000) for my proposal “Communication and Energy-Aware Autonomy for Collaborative Aerial Swarms” after a competitive evaluation round. This will allow me to continue research in the beautiful Swedish campus for two years! I am looking forward to establish new collaborations in multi-agent RL, autonomous driving, and aerial fleet control. |
|---|---|
| Jan, 2024 | I joined the department of Intelligent systems engineering at the Indiana University as a full-time visiting lecturer in Machine Learning. |
| Dec, 2023 | Honored to be the student speaker at the Luddy School of Informatics, Computing and Engineering’s winter graduation celebration. I focused on our responsibility toward the public on designing responsible and inclusive AI (News Story, Video). |
| Nov, 2023 | Successfully defended my Ph.D. dissertation titled “Cooperative Multi-Agent Autonomy Under Communication Uncertainties for Aerial Robot Fleets”. |
| Oct, 2023 | Gave an invited talk at the University of Cambridge, UK. Thanks for inviting me, Prof. Amanda Prorok. |
Selected Research Projects
Graph Attention Aerial Fleet Coordination
This work propose a multi-step partially-observable stochastic game formulation for coordinating fully-autonomous heterogeneous eVTOL fleet with graph-attention multi-agent reinforcement-learning (MARL). The paper got accepted to Robotics: Science and Systems, 2023 . [Paper].
Graphical Game-Theoretic Communication-Aware Coverage
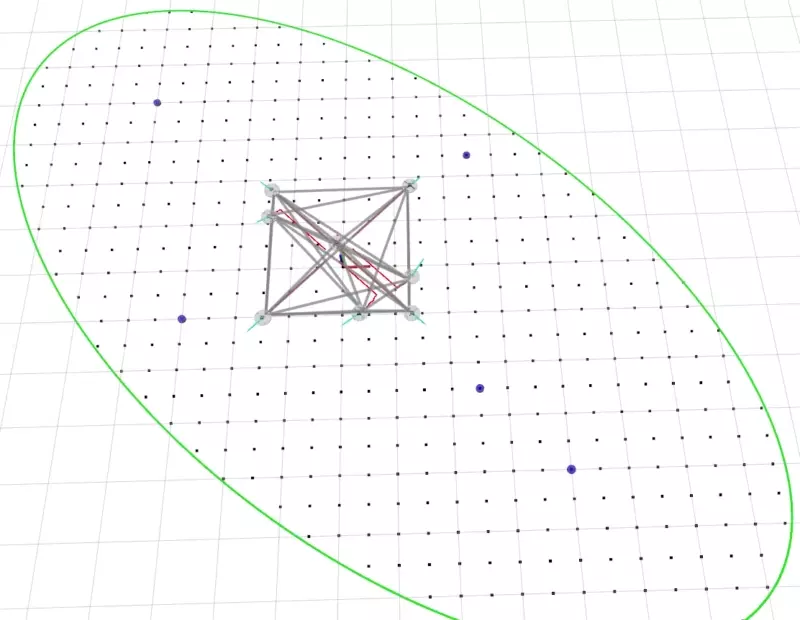
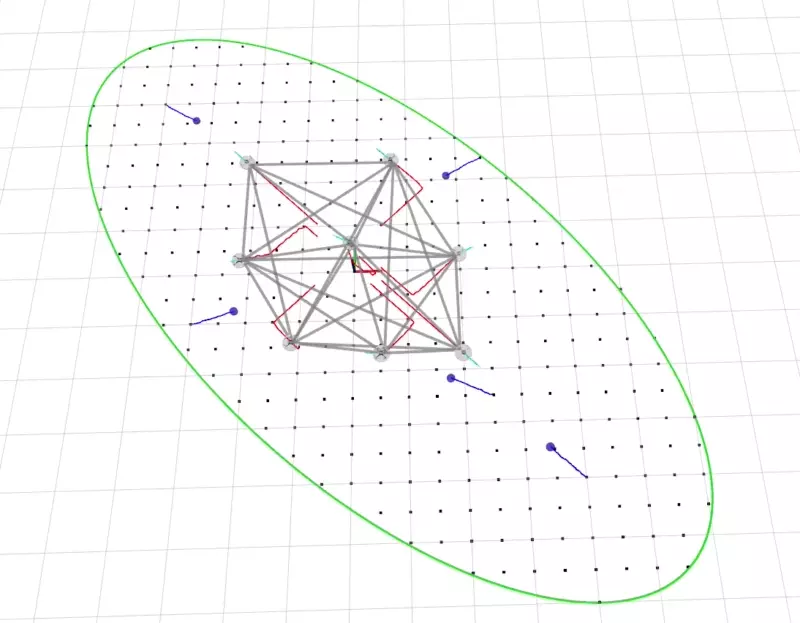
Wireless communication plays a crucial role in distributed coordination control of robot swarms. In this work we propose a robust, real-time coverage control approach for UAV swarms to provide the wireless coverage for a ground robot team using a UAV team operating over large geographic region with the local communication. The two images show a static and mobile ground robot team, where the UAV fleet is changing their formation to maximize the coverage for the ground robots. The dynamic communication links among the UAVs are shown in grey.
Checkout the full demo on Youtube .
Real-Time Distributed Flocking Control
Murmurations are one of the most beatiful natural phenomena in the world, and characterizes the perfect swarm . In this work I tried to recreate the flocking characteristics UAVs using a variational inference approach in a distributed manner. The drones only uses their local observations to infer the control actions from feasible set; which makes this approach unique compared to the literature which we can guarantee the covergence and the dynamical feasibility.
Checkout the full demo on Youtube .


Multi-UAV Formation Control
Drone formation control has been gaining a lot of attention lately with applications ranging from entertainment to and defense industries. In this work I propose a rigid-body-based formation controlling approach with drone aggressive trajectory generation. The drones showed the ability to move at 2.5ms-1 (over 10 body-lengths a second) in a user defined formation with real-time receding horizon trajectory planning.
Checkout the formation control demo on Youtube .
Checkout the minimum-jerk trajectory generation demo on Youtube .


Selected Publications
-
 Graph Attention Multi-Agent Fleet Autonomy for Advanced Air Mobility2023
Graph Attention Multi-Agent Fleet Autonomy for Advanced Air Mobility2023 -
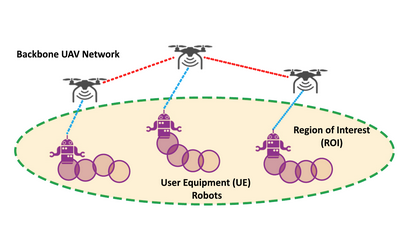 CoCo Games: Graphical Game-Theoretic Swarm Control for Communication-Aware CoverageIEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2022
CoCo Games: Graphical Game-Theoretic Swarm Control for Communication-Aware CoverageIEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2022 -
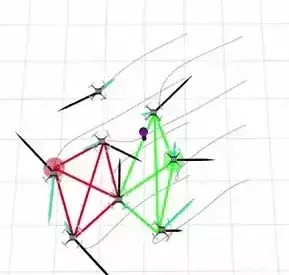 Online flocking control of UAVs with mean-field approximationIn 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2021
Online flocking control of UAVs with mean-field approximationIn 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2021 -
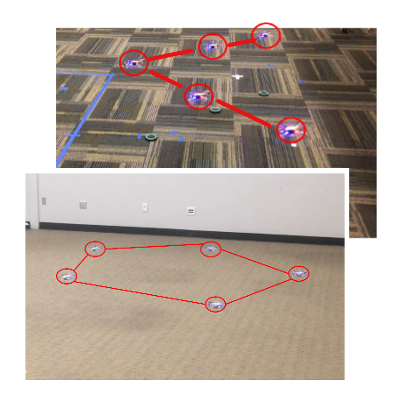 Formation control and navigation of a quadrotor swarmIn 2019 International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (ICUAS), 2019
Formation control and navigation of a quadrotor swarmIn 2019 International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (ICUAS), 2019
